Environ 6 résultats pour « Limace »
-

Limace
Limace est un nom vernaculaire ambigu désignant en français certains gastéropodes sans coquille externe appartenant à l'infra-ordre des Stylommatophora. Les limaces mesurent de 1 à 30 cm. Comme les autres gastéropodes, elles ont quatre tentacules dont deux qui ont des yeux. Les autres sont utilisés pour capter les odeurs et sont sensibles aux goûts. Elles peuvent être phytophages ou carnivores. Les plus grandes limaces sont aussi appelées des loches. Il existe des animaux aquatiques d'aspect approchant, dits limaces de mer et lièvres de mer, avec lesquels il ne faut pas les confondre.
-

-
- Artiste(s) :
- Yvonne Jean-Haffen
Feuillet double : (Page 1, 2, 3, 4, ) orage dans le jardin …
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Dessin
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Basse-cour d'élevage
- Columba (genre)
- Construction mécanique
- Coq
- Escargot
- Foudre
- …
-
- Datation :
- XXe siècle
-
-

-

Série de six gravures de contes de fées (titre factice)
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Estampe
- Ethnologie
-
- Datation :
- XIXe siècle
- XVIIIe siècle
-
-
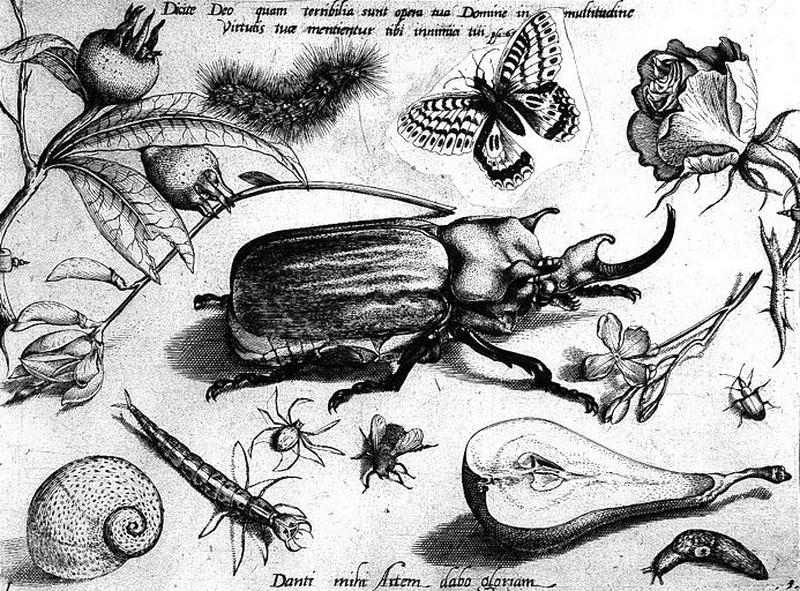

-
- Artiste(s) :
- Jacob Hoefnagel
- Joris Hoefnagel
Insectes, fruits et fleurs
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Estampe
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Araneae
- Chenille (lépidoptère)
- Escargot
- Fleur
- Fruit (botanique)
- Insecte
- …
-
- Datation :
- XVIIe siècle
-
-
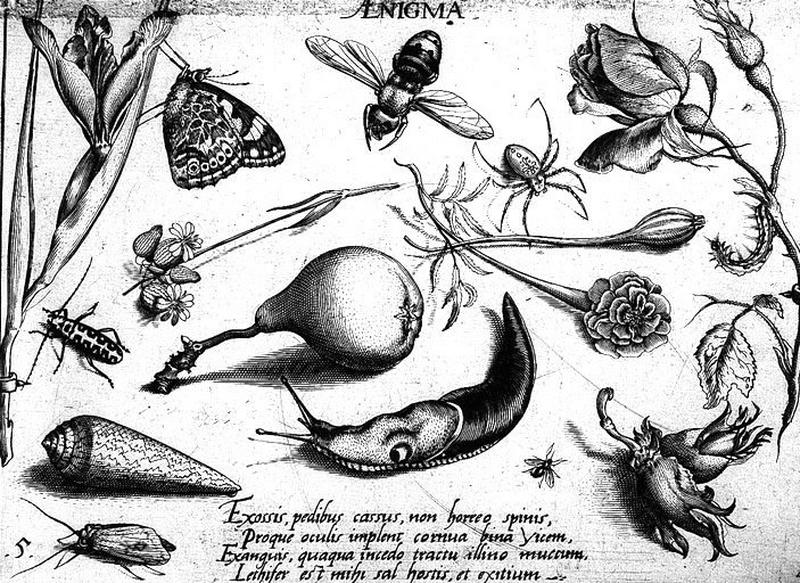

-
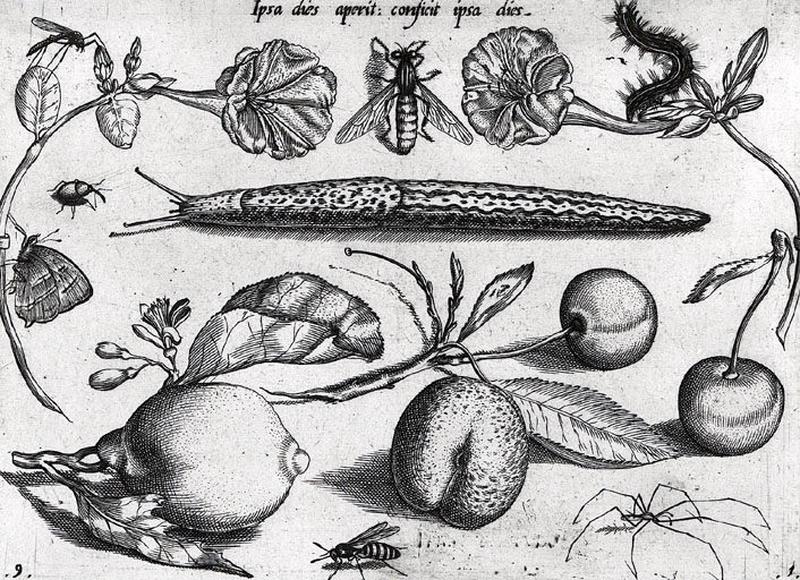
- Artiste(s) :
- Jacob Hoefnagel
- Joris Hoefnagel
Insectes, fruits et fleurs
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Estampe
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Araneae
- Fleur
- Fruit (botanique)
- Insecte
- Lepidoptera
- Limace
-
- Datation :
- XVIIe siècle
-
-
-
- Artiste(s) :
- Jacob Hoefnagel
- Joris Hoefnagel
Insectes, fruits et fleurs
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Estampe
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Araneae
- Cerise
- Chenille (lépidoptère)
- Fleur
- Fruit (botanique)
- Insecte
-
- Datation :
- XVIIe siècle
-
