Environ 20 résultats pour « Géographie »
-

Géographie
La géographie (du grec ancien γεωγραφία – geographia, composé de "η γη" la Terre et "γραφειν" décrire) est l'étude de la planète, ses terres, ses caractéristiques, ses habitants, et ses phénomènes. Une traduction littérale serait « décrire ou à écrire sur la Terre ». La première personne à utiliser le mot « géographie » était Ératosthène (276-194 avant J. -C. ) pour un ouvrage aujourd'hui perdu mais l'arrivée de la géographie est attribuée à Hérodote (484-420 avant J. -C); aussi considéré comme étant le premier historien. Pour les Grecs, c'est la description rationnelle de la Terre. Il s'agit d'une science qui répond à une curiosité nouvelle, et qui va déterminer la géopolitique en définissant les territoires à conquérir et à tenir. Pour Strabon, c'est la base de la formation de celui qui voulait décider. Quatre traditions historiques dans la recherche géographique sont l'analyse spatiale des phénomènes naturels et humains (la géographie comme une étude de la répartition des êtres vivants), des études territoriales (lieux et régions), l'étude des relations entre l'Homme et son environnement, et la recherche en sciences de la terre. Néanmoins, la géographie moderne est une discipline englobante qui cherche avant tout à mieux comprendre notre planète et toutes ses complexités humaines et naturelles, non seulement où les objets sont, mais comment ils ont changé et viennent à l'être. Longtemps les géographes ont perçu leur discipline comme une discipline carrefour (Jacqueline Bonnamour), « pont entre les sciences humaines et physiques ». Une division de la géographie en deux branches principales s'est imposée à l'usage, la géographie humaine et la géographie physique. Cependant la géographie reste par excellence une discipline de synthèse qui interroge à la fois « les traces » laissées par les sociétés (mise en valeur des espaces) ou la nature (orogenèse des montagnes, impact du climat…) et les dynamiques en oeuvre aussi bien dans les sociétés (émergence socio-économique de la façade asiatique pacifique, désindustrialisation progressive des pays développés à économie de marché) qu'au sein de l'environnement physique (« Global Change », montée du niveau marin…). La géographie s'intéresse donc à la fois aux héritages (physiques ou humains) et aux dynamiques (démographiques, socio économiques, culturelles, climatiques, etc. ) présents dans les espaces. Par ailleurs cette discipline intègre de plus en plus divers champs culturels tels que la peinture paysagiste, le roman ou encore le cinéma.
-

-
- Artiste(s) :
- Anonyme
HOMME DE L'ILE DE PAQUES.CHEF DE L'ILE DE STE. CHRISTINE (t…
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Estampe
- Ethnologie
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Couvre-chef
- Homme
- Plume
-
- Datation :
- XIXe siècle
-
-

LE BARDE...LA GEOGRAPHIE (titre inscrit)
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Estampe
- Ethnologie
- Moyen Âge
-
- Datation :
- XIXe siècle
-
-

Il est plus difficile d'enseigner que d'apprendre (titre in…
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Estampe
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Enseignement
- Géographie
- Instituteur
- Lecture
- École
-
- Datation :
- XIXe siècle
- XXe siècle
-
-

-
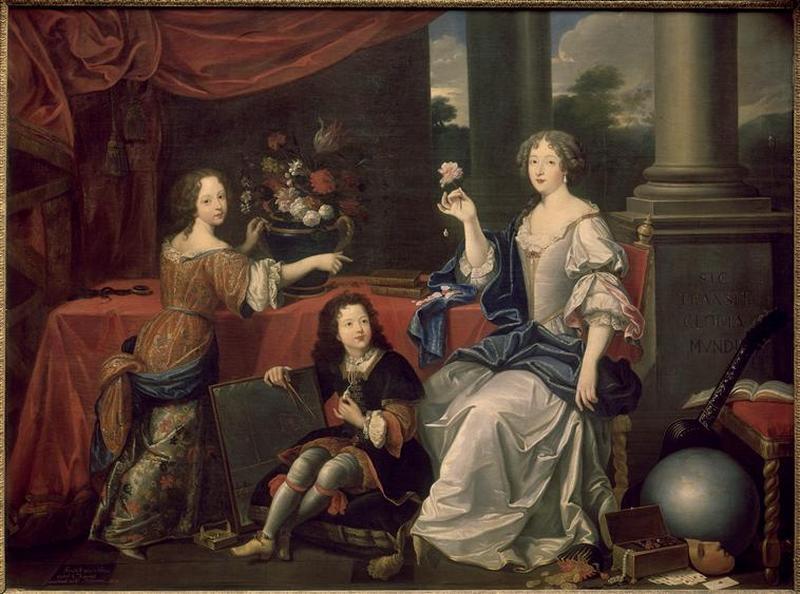

-
- Artiste(s) :
- Pierre Mignard
Louise-Françoise de la Baume le Blanc, duchesse de la Valli…
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Peinture
-
- Datation :
- XIXe siècle
-
-
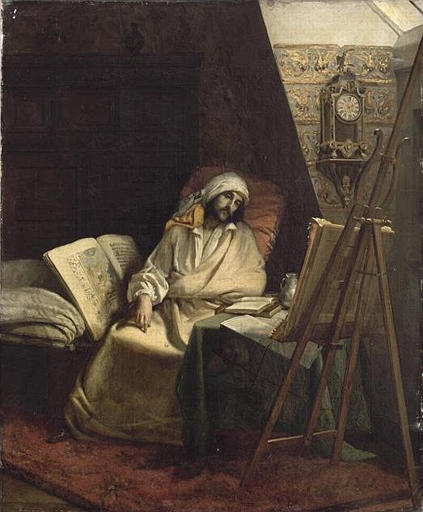

ARTISTE MALADE
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Peinture
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Armoire
- Artiste
- Carte géographique
- Enluminure
- Géographie
- Homme
- …
-
- Datation :
- XIXe siècle
-
-

GLORIFICATION DE L'EUCHARISTIE : ANGES ET FIGURES ALLEGORIQ…
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Peinture
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Allégorie
- Ange
- Astronomie
- Calice (liturgie)
- Compas (géométrie)
- Eucharistie
- …
-
- Datation :
- XVIIe siècle
-
-

-
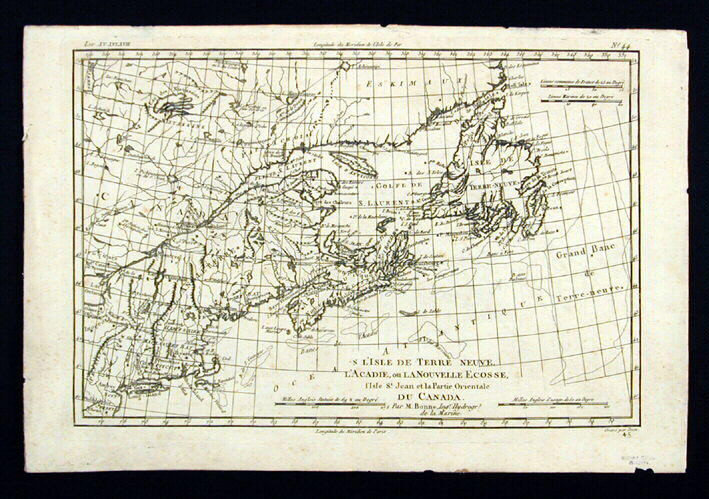
-
- Artiste(s) :
- Rigobert Bonne
L'Isle de Terre-Neuve, l'Acadie ou la Nouvelle Ecosse, l'Is…
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Carte géographique
- Ethnologie
- Pays basque
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Canada
- Carte géographique
- Nouvelle-Écosse
- Terre-Neuve
-
- Datation :
- XVIIIe siècle
-
-
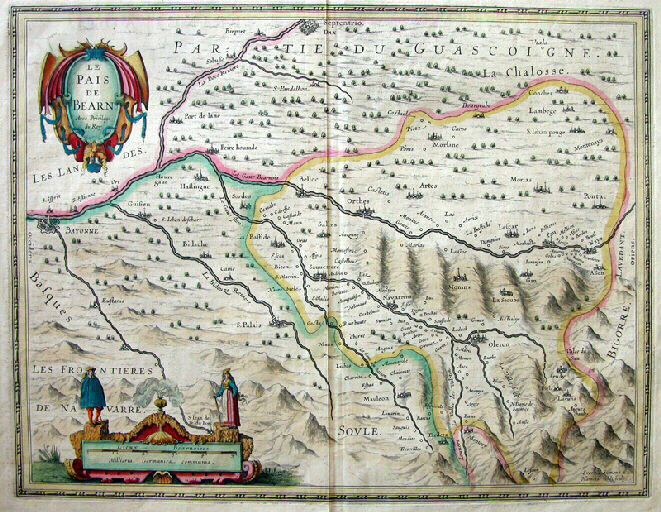
LE PAIS DE BEARN
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Carte géographique
- Ethnologie
- Pays basque
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Carte géographique
-
- Datation :
- XVIIe siècle
-
-

-
- Artiste(s) :
- Anonyme
Allégorie de la Géographie
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Dessin
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Allégorie
- Femme
- Géographie
- Sphère
- Station assise
-
- Datation :
- XVIIe siècle
-
-
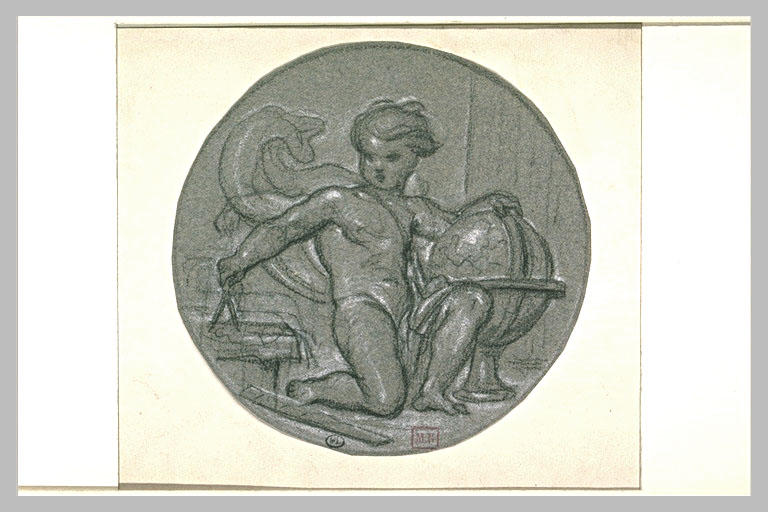

-
- Artiste(s) :
- Félix-Joseph Barrias
Enfant nu, tenant une sphère et un compas
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Dessin
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Allégorie
- Compas (géométrie)
- Enfant
- Géographie
- Nu (genre artistique)
- Sphère
-
- Datation :
- XIXe siècle
- XXe siècle
-
-

Etude de la géographie et de l'astronomie
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Dessin
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Allégorie
- Astronome
- Astronomie
- Endymion
- Géographe
- Géographie
- …
-
- Datation :
- XVIe siècle
-
-

-
- Artiste(s) :
- Charles Cressent
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Meuble
-
- Désignation :
- armoire
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Allégorie
- Arabesque (beaux-arts)
- Commerce
- Enfant
- Géographie
-
- Datation :
- XVIIIe siècle
-
-

-
- Artiste(s) :
- Jean-Démosthène Dugourc
- Manufacture nationale de Sèvres
Pendule aux Vestales
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Céramique
- Métrologie
-
- Datation :
- XVIIIe siècle
-
-
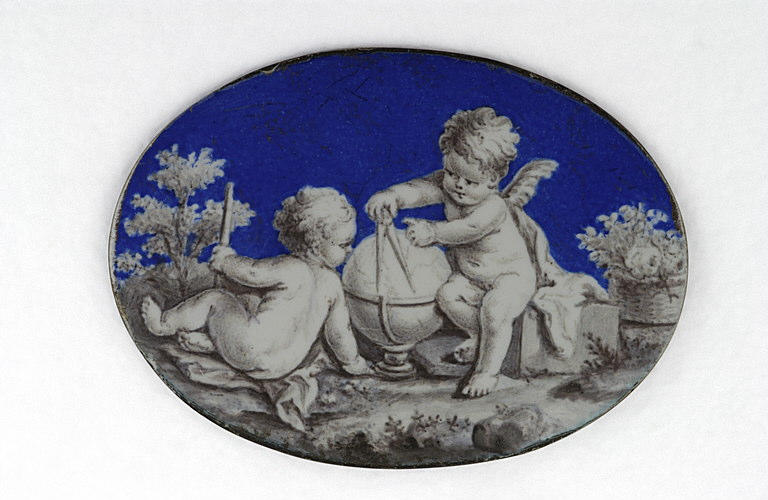

-
- Artiste(s) :
- Anonyme
Un enfant nu et un amour font des calculs avec un compas
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Miniature (portrait)
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Allégorie
- Compas (géométrie)
- Enfant
- Géographie
- Géométrie
-
-
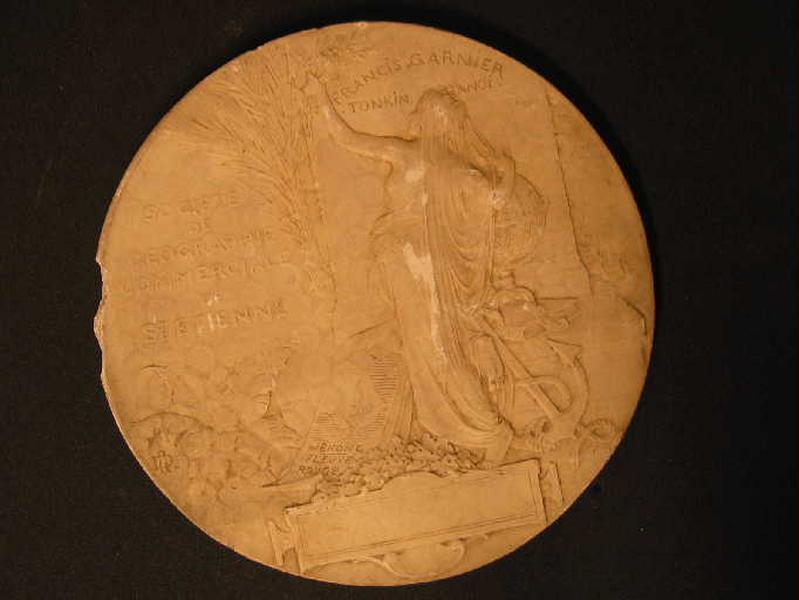

Portrait de Francis Garnier
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Numismatique
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Allégorie
- Ancre (mouillage)
- Branche (botanique)
- Géographie
- Laurus nobilis
- Portrait
-
- Datation :
- XIXe siècle
-
-
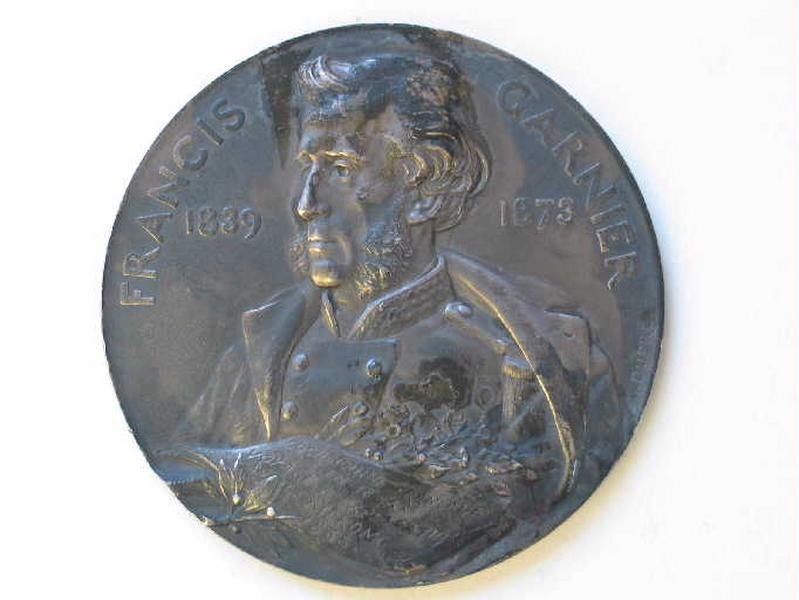

Portrait de Francis Garnier
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Numismatique
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Allégorie
- Ancre (mouillage)
- Branche (botanique)
- Géographie
- Laurus nobilis
- Médaille
- …
-
- Datation :
- XIXe siècle
-
-
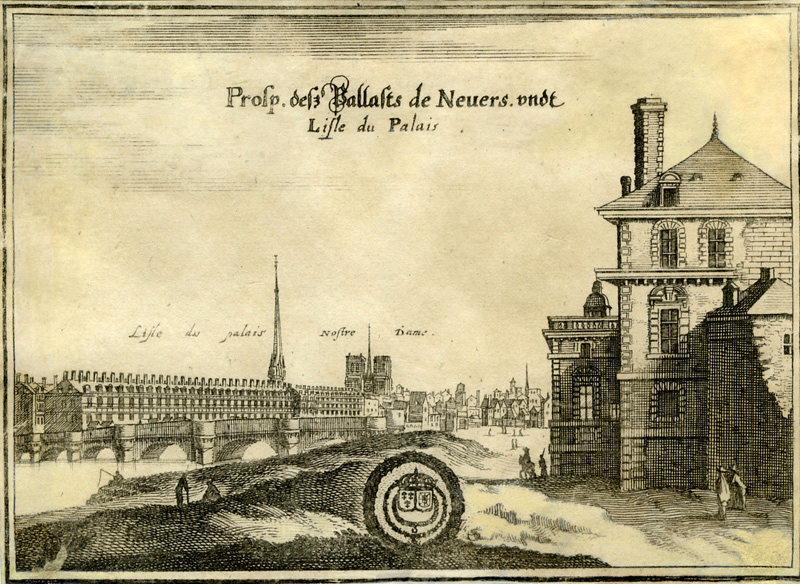

Hôtel de Nevers à Paris
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Estampe
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Cathédrale
- Clocher
- Hôtel particulier
- Palais
- Paris
- Paysage
-
- Datation :
- XVIIe siècle
-
-
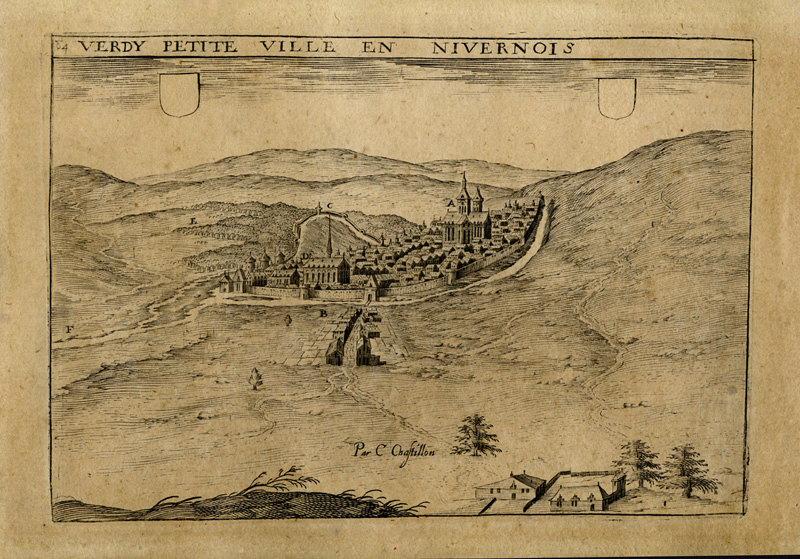

-
- Artiste(s) :
- Anonyme
Verdy petite ville en Nivernois
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Estampe
-
- Datation :
- XVIIe siècle
- XVIe siècle
-
-

Moulins-Engilbert
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Estampe
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Fortification
- Moulins-Engilbert
- Paysage
- Rempart
- Rivière
- Ville
-
- Datation :
- XVIIe siècle
-
-

Langeron - la Ferté Langeron
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Estampe
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Château
- Langeron (Nièvre)
- Pont
- Rivière
-
- Datation :
- XIXe siècle
-
-
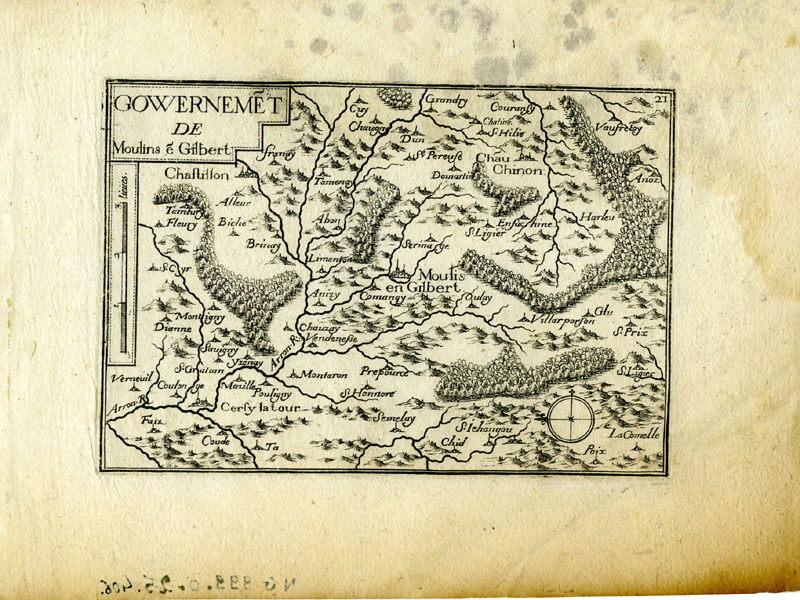
Gouvernement de Moulins-Engilbert
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Carte géographique
- Estampe
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Carte géographique
- Moulins-Engilbert
-
- Datation :
- XVIIe siècle
-
-
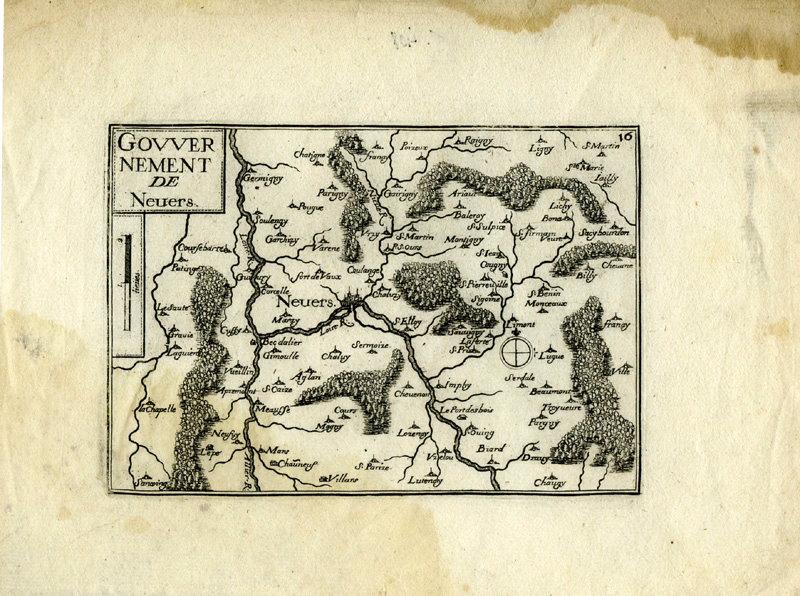
Gouvernement de Nevers
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Carte géographique
- Estampe
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Carte géographique
- Nevers
-
- Datation :
- XVIIe siècle
-
-
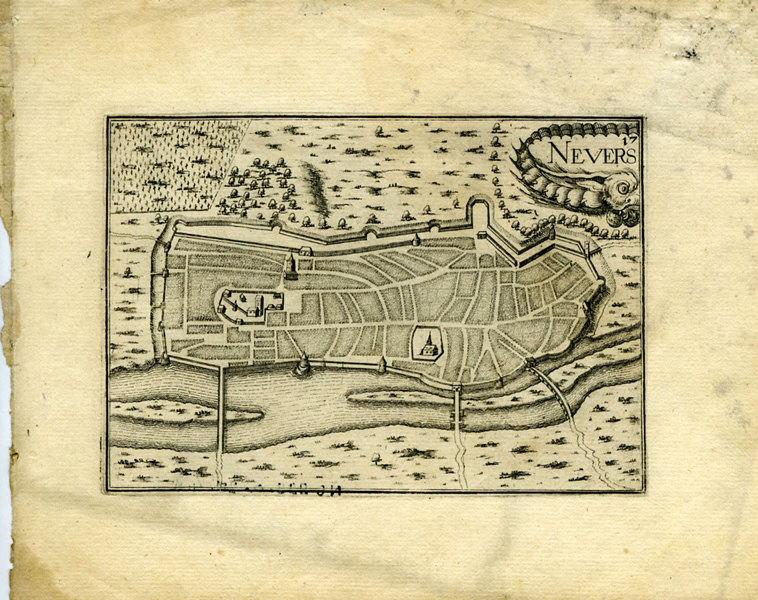
Nevers
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Carte géographique
- Estampe
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Fortification
- Loire
- Nevers
- Ville
-
- Datation :
- XVIIe siècle
-
-
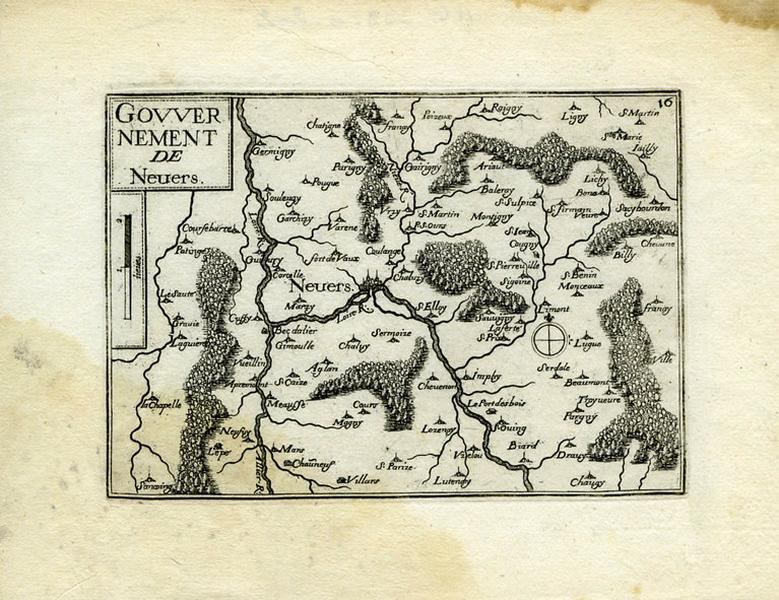
Gouvernement de Nevers
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Carte géographique
- Estampe
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Carte géographique
- Nevers
-
- Datation :
- XVIIe siècle
-
-

Plan et profils des villes de la Loire
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Carte géographique
- Estampe
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Amboise
- Angers
- Bateau
- Blois
- Carte géographique
- Fortification
- …
-
- Datation :
- XVIIe siècle
-
