Environ 10 résultats pour « Haïti »
-

Haïti
Haïti, en forme longue la République d'Haïti, en créole haïtien Ayiti et Repiblik Dayiti, est un pays des Grandes Antilles occupant le tiers occidental de l'île d'Hispaniola (soit 27 750 km environ). Sa capitale est Port-au-Prince et son point culminant est le pic la Selle. La révolte des esclaves de Saint-Domingue est à l'origine de la création de la République d'Haïti qui devient en 1804 la première république indépendante de population majoritairement noire après l'abandon forcé de l'île par l'armée de Napoléon Bonaparte. Haïti est aussi le seul pays francophone indépendant des Caraïbes. C'est aussi le premier pays Noir à prendre son indépendance sans bénéficier d'une aide extérieure. Haïti est un pays en voie de développement, qui fait une expérience de démocratie naissante et qui tente de s'organiser et de se reconstruire après le violent séisme qui a dévasté un tiers de son territoire. Avec pourtant les mêmes conditions naturelles de départ que sa voisine, la République dominicaine, qui comparativement vit plutôt bien grâce au tourisme, Haïti a occupé la première destination touristique de la caraïbe dans les années 1950, 1960 et 1970. Surnommé "La Perle des Antilles", il fut un temps le pays le plus visité des Antilles.
-

TOUSSAINT LOUVERTURE (titre inscrit)
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Estampe
- Ethnologie
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Haïti
- Homme
- Président de la République
- Race humaine
- Toussaint Louverture
-
- Datation :
- XIXe siècle
-
-

-
- Domaine(s) :
- Céramique
- Ethnologie
- Production domestique
-
- Désignation :
- bouteille
-
- Datation :
- XIXe siècle
-
-

-
- Domaine(s) :
- Céramique
- Ethnologie
- Production domestique
-
- Désignation :
- bouteille
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Fleur
-
- Datation :
- XIXe siècle
-
-

-
- Domaine(s) :
- Céramique
- Ethnologie
- Production domestique
-
- Désignation :
- bouteille
-
- Datation :
- XIXe siècle
-
-

-
- Domaine(s) :
- Céramique
- Ethnologie
- Production domestique
-
- Désignation :
- bouteille
-
- Datation :
- XIXe siècle
-
-
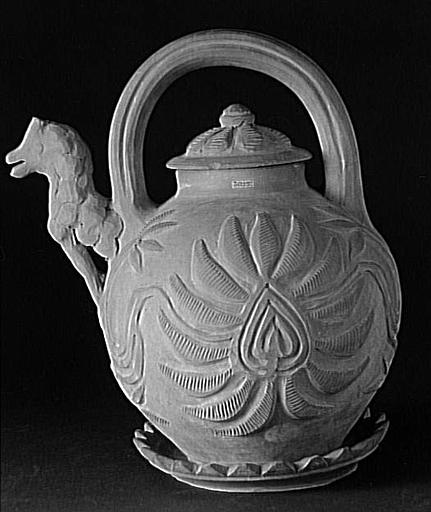

-
- Domaine(s) :
- Céramique
- Ethnologie
-
- Désignation :
- théière (?, zoomorphe)
-
- Datation :
- XIXe siècle
-
-
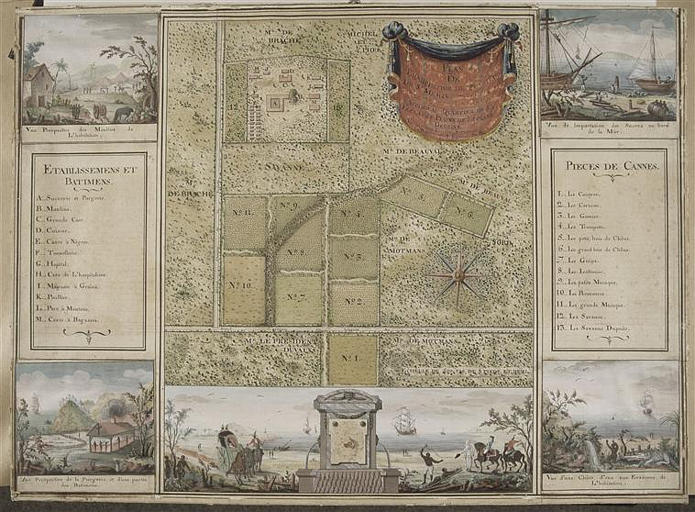
Plan de l'habitation de Févret de Saint-Mémin à Saint-Domin…
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Carte géographique
- Dessin
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Alligator
- Arecaceae
- Chute d'eau
- Fabrication
- Haïti
- Individu
- …
-
- Datation :
- XVIIIe siècle
-
-

CHARLES VICTOR EMMANUEL LECLERC, GENERAL EN CHEF DE L'ARMEE…
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Peinture
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Général
- Haïti
- Homme
- Saint-Domingue (ville)
-
- Datation :
- XIXe siècle
-
-
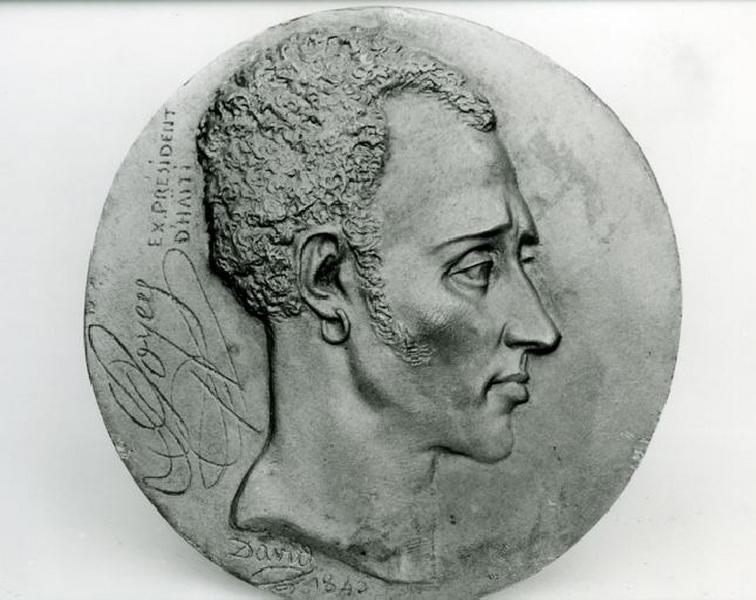

-
- Artiste(s) :
- Pierre-Jean David d'Angers
JEAN PIERRE BOYER (1776-1850)
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Sculpture
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Haïti
- Homme
- Nu (genre artistique)
- Portrait
-
- Datation :
- XIXe siècle
-
-
-
- Artiste(s) :
- Gustave Moreau
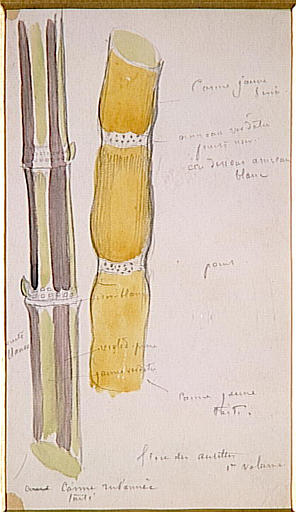
Etude de plantes
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Dessin
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Canne à sucre
- Haïti
-
- Datation :
- XIXe siècle
-
-

69 dessins pour l'illustration de l'Histoire de France sous…
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Dessin
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Courrier
- Haïti
- Toussaint Louverture
-
- Datation :
- XIXe siècle
-
-

AMERIQUE. (titre inscrit)
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Estampe
- Ethnologie
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Amérindiens
- Amérique
- Arc (arme)
- Arecaceae
- Canada
- Carquois
- …
-
- Datation :
- XIXe siècle
-
-

-
- Artiste(s) :
- Anonyme
Le caoutchouc. 1 (titre inscrit)
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Estampe
- Ethnologie
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Boisson
- Caoutchouc (matériau)
- Homme
- Hutte
-
- Datation :
- XXe siècle
-
-

-
- Artiste(s) :
- Pierre Ozanne
Vue du Cap Français, prise du mouillage le soir, en 1771
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Dessin
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Haïti
- Paysage
- Saint-Domingue (ville)
-
- Datation :
- XIXe siècle
- XVIIIe siècle
-
-

Fabre Geffrard, président d'Haïti
-
- Domaine(s) :
- Estampe
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Haïti
- Portrait
- Président de la République
-
- Datation :
- XIXe siècle
-
-
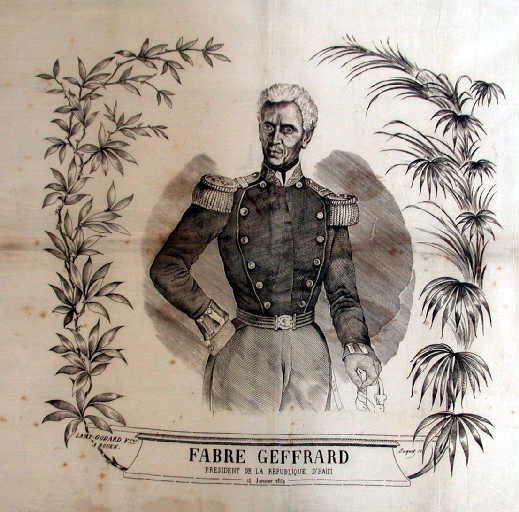

Fabre Geffrard, Président de la République d'Haïti. Le 15 j…
-
- Sujet représenté :
- Haïti
- Portrait
- Président de la République
-
- Datation :
- XIXe siècle
